Advocating for Children’s Rights and Well-Being
An Interfaith Approach
A Guide Jointly Developed by the Prayer and Action for Children and Global Network of Religions for Children Initiatives of Arigatou International

The Guide at a Glance
What is this publication?
What is this publication?
What is it designed to do?
What is it designed to do?
- To inspire and encourage the advocacy work of the GNRC members and faith-inspired organizations working to promote children’s rights and well-being;
- To offer a user-friendly interfaith approach to advocacy for children’s rights and well-being which builds on the meaning, value, and inter-connectedness of prayer and action; and
- To support the quality of faith-inspired advocacy for children and improve its outcomes at the local and national levels.
What are the desired outcomes of the approach to advocacy proposed in this guide?
What are the desired outcomes of the approach to advocacy proposed in this guide?
- All children enjoy all their rights
- All children enjoy physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being
- The achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030
Who developed this guide to interfaith approach to advocacy, and how?
Who developed this guide to interfaith approach to advocacy, and how?
Who is this guide for?
Who is this guide for?
Why was it developed?
Why was it developed?
The meaning and value of prayer and action in the world’s major religions
There are many definitions of prayer, and various forms of worship and meditation practiced by the world’s diverse religious and faith traditions, but there are many common threads found across traditions. For people of faith, prayer and meditation are powerful, both for the one who practices them and for the world in which he or she lives. The practice of prayer, whatever its form, including meditation and reflection, transcends generations, cultures, and barriers. Prayer, especially when considered in the light of our common human call and responsibility to care for our neighbor, as we would like him or her to care for us, is ultimately about cultivating our connection with the presence of the Divine.


Religious leaders and faith-based organizations, scholars and theologians place high value on including action in the prayerful and spiritual life of their communities.
Scriptures and holy writings from diverse religious traditions tell us that prayer leads us to the knowledge that we are inter-connected and to an awareness of the needs of others, that prayer removes the negative character traits, that acts of kindness to others in need will be rewarded, that believers must be intentional about the words of their prayers and meet the obligations therein, 12 and that service is prayerful action.
The meaning and value of interfaith prayer and action for children
Arigatou International recognizes and promotes the value added by the inter-connectedness of prayer and action in its work to encourage diverse faith communities and faith-inspired organizations to work together to protect all children’s rights and bring an end to all forms of violence against children:
For centuries, churches, synagogues, Buddhist temples, ashrams, mosques, and other religious institutions have been involved in life-saving work for the common good of children. Religious communities have a very particular understanding that to work for the common good requires consciousness of care, compassion, and empowerment of all children in every nation and every community. Many people believe that without this, it is simply not possible to work effectively for the common good.
Many of the great contributions made by particular faith communities and faith-inspired organizations to promoting children’s rights and protecting them from violence are well known. What is lesser appreciated is the significant value-added when diverse religious communities come together to pray and take collaborative action, and how this specifically contributes to children’s well-being and development.

Advocacy for Children
The Guide uses the term “advocacy for children” in its broadest sense, for any systematic, organized action to influence changes in laws, policies, practices, social norms or systems, at any level, aiming to ensure that all children can enjoy all their rights and to preserve and promote their physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being. This advocacy is a process that generates greater awareness and momentum around issues facing children that need more attention from decision-makers.
The interfaith approach to advocacy for children proposed in the Guide
This approach represents a way for diverse faith communities and faith-inspired organizations to express the inward, contemplative dimension of prayer and meditation, and the outward volitional dimension of action in, joint efforts to catalyze sustainable and transformative change for children. Thus, “prayer” and “action” are seen as woven into every step of the process.
*Hover over the different elements to learn more details on each level of the approach
*Click on the different elements to learn more details on each level of the approach




Change in Attitudes, Social Norms and Behaviors.
Faith plays a significant role in the lives of a majority of the world’s population, throughout the entire life course. It has a deep impact on personal and collective values and social norms, 5 which influence the way people behave.
1 of 3
Change in socioeconomic systems and safety nets.
Effective advocacy should also result in changes to systems, particularly at the community level. This includes influencing changes that will strengthen people’s personal, socioeconomic opportunities and assets (both internal and external), especially those that impact children’s lives and well-being. It also includes influencing positive changes to community-based mechanisms that provide support for children and safety nets that help disadvantaged families nurture, protect and provide for their children.
2 of 3
Change in legislation, policy and budgets.
An interfaith approach to advocacy for children can focus on promoting a review of legal and policy frameworks, or on monitoring resource allocation and expenditure for children’s rights, at national and/or decentralized levels, to make sure that these decisions are affirming the dignity of each and every child, while empowering children and the community to have a voice in the decisions that concern them.
3 of 3
Engage
It is about highlighting the shared responsibility we all have with regard to children’s rights and well-being and, particularly, broadening the support for these from faith communities and faith-inspired organizations.
This shared responsibility implies:
- Encouraging the promotion and protection of children’s rights by all stakeholders that have some level of responsibility (parents, teachers, community leaders, etc.), from a holistic perspective which includes children’s spiritual well-being;
- Holding States accountable for breaches in children’s rights by affirming the human dignity of each and every person, and by promoting spaces and opportunities for children to claim their rights; and
- Including the vital spiritual component that helps to transform not just actions but hearts.

Stand
By encouraging interfaith dialogue, the common interests and shared values of the diverse faiths involved will emerge; trust and respect among the participants will be established; and a common narrative can then be developed, aimed at creating a more inclusive and sustainable world for children, where no boy or girl is left behind. 2 of 9
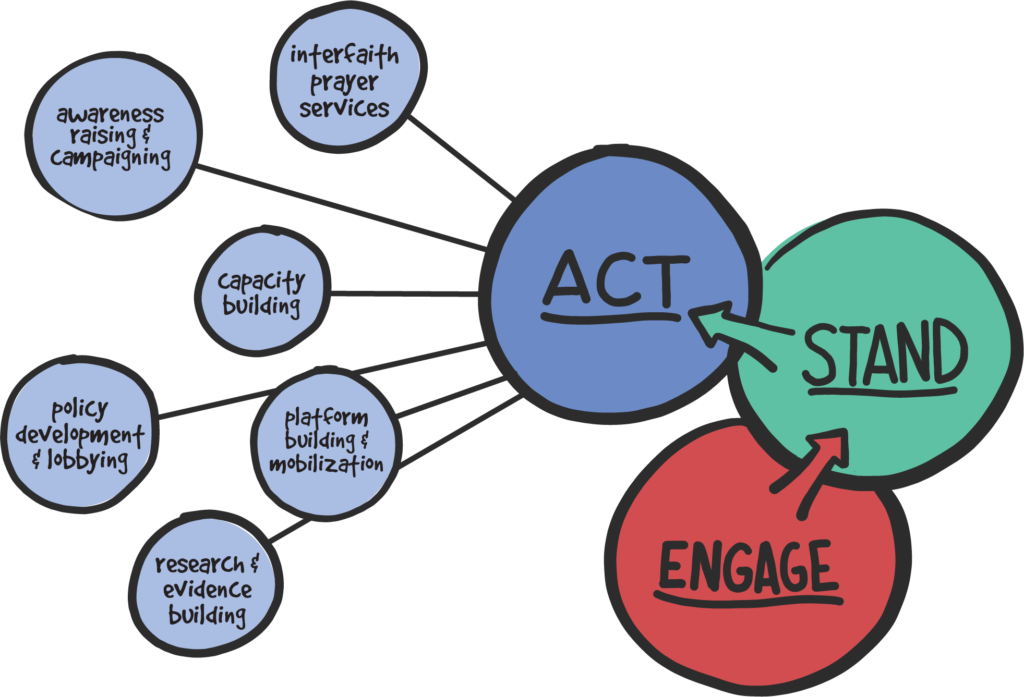
Act
The approach focuses on influencing change at three levels, each of which is critical to promoting children’s rights and well-being:- Attitudes, social norms, and behaviors, including those about or towards children;
- Socioeconomic systems and community safety nets; and
- Legislation, policy and budgets.

Interfaith Prayer Services
Interfaith prayer services can be a powerful opportunity to bring people together from across religious and spiritual traditions; to serve as a platform to respect and value multi-religious and spiritual beliefs and to pray or meditate for a common cause; to provide a visual and spiritual representation of interfaith dialogue for a shared vision of children; and to prioritize children’s dignity, their right to flourish in peaceful, safe and caring environments, and recognize and support their precious role in society. 4 of 9
Campaigning and awareness raising
The main advantages of campaigning are that it enables the simultaneous use of different actions (e.g., panel discussions, mass communication events, statements and press releases); engagement with multiple stakeholders; and inter-generational participation (e.g. interfaith prayer services with participation by both adults and children). Other ways to raise awareness include public processions, symbolic actions (e.g., street dramas, photo/art exhibitions, wearing wristbands), and petitions. 5 of 9
Capacity building
Capacity building brings enormous benefits to advocacy goals related to behavior change and change of systems, as it encourages reflection, exchange, learning, and contextual approaches to challenges and opportunities to promote change. In addition, participating in capacity-building workshops sometimes provides opportunities to meet like-minded people from other communities and to network with organizations who may wish to collaborate in future. 6 of 9
Policy development and lobbying
Participating in policy development processes requires lobbying key policymakers at local or national levels that have the power to influence the outcome of the process (e.g., parliamentarians). 7 of 9
Platform building and mobilization
Participation in platforms for advocacy can help to take advocacy messages further and deeper. However, the process of developing these collaborations can take multiple forms including alliances, coalitions, partnerships, or networks. All of these platforms use collaborative methods to achieve specific goals. Mobilization could be in the form of face-to-face or online. The latter requires strategic thinking and planning about what information is relevant to communicate, to which audiences, and via which platforms and channels. Which of these to use depends on the advocacy goal, messages and audience. It is important to bear in mind that not all platforms reach the same audience; demographic information on the main social media platforms can be a useful starting point to assess the best channel for online mobilization. 8 of 9
Research and evidence building
Evidence-based messages are more powerful and result-oriented than statements that are not supported by information that makes the issue relevant. The involvement of faith communities and faith-inspired organizations in research is an advocacy action with enormous potential to bring faith perspectives into analysis and decision-making processes to address child rights issues; but most importantly, to promote interfaith dialogue and collaboration for children’s rights and well-being. 9 of 9
Developing an Advocacy Strategy
STEP 1
Identifying and prioritizing the advocacy issue
When identifying and prioritizing the advocacy issue for local action, it is important to assess what change would be most relevant based on the evidence available, the situation of the community or group that could benefit from the advocacy efforts, and the socio-political environment. Selecting and articulating clearly the advocacy issue locally is very important because it marks the route for action. As a route, the more specific and focused it is, the better chance there is to reach the destination.
STEP 2
Analyzing the root causes
Root causes respond to the why of the issue and could be related to multiple structural, cultural, social, historical, or economic factors, some of which may at times seem beyond our reach to transform. However, it is through this analysis that the best opportunities can be found to bring about positive change at one or more of the three levels of change: influencing change in attitudes, social norms, and behavior, including about and towards children; influencing change in socioeconomic systems and community safety nets; or influencing change in legislation, policy and budgets.
STEP 3
Identifying desired change, key stakeholders and partners
It is about exploring the overall vision for change; how that change will happen; and who has the power or is in the position to do something to bring about the desired change. In other words, this is when the advocacy team moves into the second component of the advocacy approach — encouraging diverse faith communities and faith-inspired organizations to dialogue about the change they would like to see and their common vision for the child, and what they can do together to help achieve a transformative change.
In advocacy, there are two important questions regarding the “who”:
- Who would we like to influence to bring about the desired change (who do we want to see thinking or acting differently)?
- Who do we want to partner with to influence that change?
STEP 4
Advocacy action planning and implementation
Good strategic planning leads to the most effective use of available resources and helps to minimize risks and maximize opportunities. This step is about planning and carrying out specific activities that will contribute to reaching the advocacy goal. It is the time for action to achieve the shared vision and goal: to influence sustainable and transformative change for the rights and well-being of children. These actions may take place with others or within faith communities, but all are guided by the shared vision.
This step forms the core of the third component of the interfaith approach to advocacy in the Guide; the time has come to go beyond dialogue to take collaborative action. Advocacy actions include a variety of options, including but not limited to interfaith prayer services, awareness raising and campaigning, capacity building, policy development and lobbying, platform building and mobilization, capacity building, and research and evidence-based advocacy.
STEP 5
Monitoring, learning, and adapting
Advocacy efforts evolve with changing contexts, messages, and actions. It is important to continuously follow-up on the progress of the advocacy efforts as the plan is being implemented; doing so creates opportunities to learn, adapt, and increase success (see the companion toolkit for further guidance on how to do it).
7 Tips from the Advocacy Guide







Download the full Advocacy Guide and it's support resource, the Companion Toolkit.
The Advocacy Guide and Companion Toolkit have been jointly developed by the Prayer and Action for Children and Global Network of Religions for Children Initiatives of Arigatou International.


